The link between SEO and Google entities has been a subject of intense research and debate among online marketing experts. Google entities have now enabled the search engine to interpret words more accurately as opposed to the old rigid ways of lexicon search. They achieve this through the knowledge graph and by creating relationships between entities to determine their relevance to the topic.
Having stated this, we do understand that deciphering the impact of entities on search engine optimization can be challenging. Our comprehensive guide, however, will make it easier for you by:
- Defining what an entity is by using examples
- Explaining how and why Google uses these entities
- Highlighting the relevance of entities to SEO
- Discussing the key SEO ranking factors
If you think keyword stuffing is still the way to rank a website in 2024, you are wrong. Since the year 2012, search engine technology has advanced and evolved steadily towards “Things, not Strings“. This means that along with the frequency of the keywords, there are now many other ways to determine what shows up in Google search. Namely Entities, and how they relate to one another. These new ranking methods lead SEO’s to shift their focus away from keywords, and look for topics. When we ‘optimize for entities’ in SEO we emphasize the use of NLP (Natural Language Processing) as an important SEO factor.
What Are Google Entities?
To truly grasp the impact of Google entities on the SEO, it is important to recognize what an entity is. In the philosophical sense, an entity is something that is concrete and not a complete intangible like a concept or idea. It is also viewed as a ‘unit’ when understood in technical terms.
Google, however, defines an entity as a concept or thing that is:
- Singular
- Unique
- Well-defined
- Distinguishable
This definition is comprehensive enough to accommodate persons, organizations, events, products, places, things, and ideas (Labeled as Other) that fulfill the criteria. In other words, a Google entity appears to be equivalent to a generic term that represents a whole semantic range of “Things” in the known world.
What Google does is that it transfers and graphs the meanings associated with a word or entity into its own Knowledge base. This is an attempt to train its search engine to understand human language in a way that is similar to how we interpret language. Therefore, an entity search emerges as a more accurate methodology for machines to recognize user search intent as it maps additional reliable sources to answer any search query.
Examples of Entities
So far, our understanding of entities makes it clear that to comprehend the semantics of a request, individual Google search queries are disintegrated into entities. Some examples of entities can be:
- People or Individuals: If you use a person as an entity, you will have to use words that can help uniquely identify the entity. Like looking up “Bill Slawski” the SEO consultant from SEO by the Sea. These words can be particular to the entity’s occupation, education, or even spouse.
- Cities and Countries: Every major city of a country, which is considered as an entity, will include appropriate semantic keywords that are specific to it. For instance, “Massachusetts” is likely to be associated with universities like “Harvard” or “MIT“.
- Organizations and Brands: Any known company treated like an entity will have text describing it in detail. An example is how a well-known entity like Microsoft will have a description with words like “Bill Gates” or “Microsoft Windows”
Give Google’s own NLP Cloud Tool a try! Take any text from a webpage and analyze the article from an entity and NLP standpoint.
How Exactly Does Google Use Entities?
We have established that Google entity search is basically meant to form associations. But why is it that Google cares so much about forming these relations? Why is the keyword frequency not enough for the search engine to understand user intent and meanings?
In the past, the Internet and search engines have dealt with unorganized and unclassified data. This unstructured data followed no pre-defined model that could extract meaning out of the data. Even though such keywords identified recurring patterns within the data, they failed to attach any meaning to those terms. The unstructured data, therefore, increased the probability of the users ending up with search results that were unrelated to their query.

Let’s take a real world example, lets say someone does a search for “Tools”, inside Google Image Search, we can see “pills” with the different entity relationships to tools, like….
- Drawing Tools
- Carpentry Tools
- Electrical Tools
- Kitchen Tools
- Individual Tools (Hammer / Wrench / Screwdriver )
- Automotive Tools
- Power Tools
- Garden Tools
- Farming Tools
- Mechanical Tools
Semantic entity search enables Google to understand the relationship between a search term (an entity) and all of the related concepts to that keyword/entity (stored in Google’s Knowledge Base). It also provides a way of structuring the data by classifying every piece of data as an entity.
The following is the process through which data (entity candidate) is identified and extracted:
- A piece of information is first detected in a document over the Internet
- The entity models stored in the KG database determine this unique and individual piece of information to be a new entity
- A known entity, contained in one or more entity models, that appears to be similar or relevant to the new entity is identified
- Then, any similar contexts between the new entity and the known entity are detected to see if the context has any relationship to the known entity
- A series of similar complex relationship detection continues until an association is confirmed and established between the entities
One of the best resources I have found on the web, about getting your own Knowledge panel is Jason Barnard’s tool, called Kalicube Pro. It is a entire suite of tools, and resources that can help you brand the SERP’s and gain more traction in the Knowledge Graph.
What’s the Point of This?
Semantic SEO or entity optimization is the process of organizing data in a way that is easy for search engines to interrupt for machines. Data that is composed of large amounts of unstructured information can be lost in the very growing sea of web content. One of my favorite things to include in entity SEO optimization is advanced schema markup. Sometimes just using the entities on-page may not be enough for Google to “recognize them”. One of my dear friends, and titan in the Entity SEO space, Dixon Jones gives us a direct tool to detect entities from your on-page copy. Using schema with your on-page SEO, is solid path to get Google to better understand and recognize on-page entities, because its created in a language (JSON-LD) created directly by the search engines themselves. Because this script is directly injected into the DOM, with a full list of entities, this structured data turns out to be reliable and verified very quickly by Google.
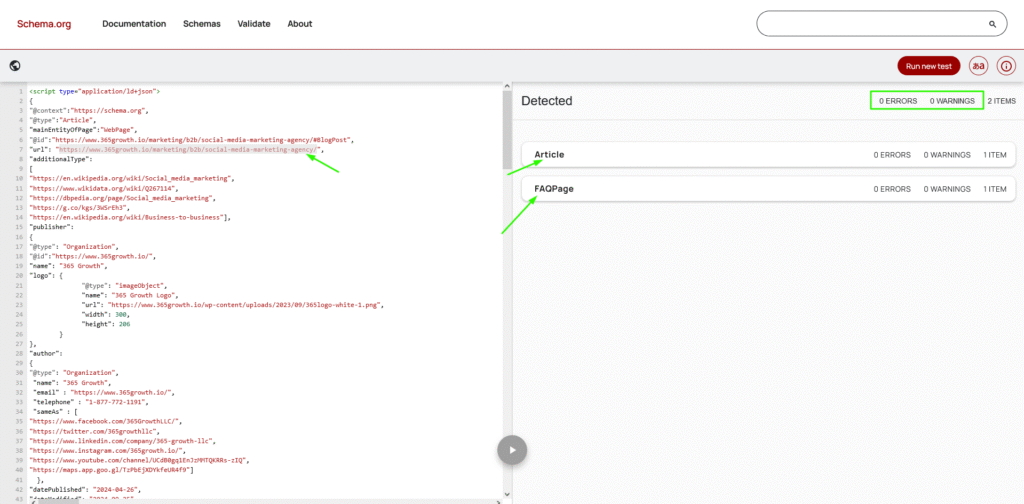
Google’s new understanding of how entities relate to one another, helps you in mundane tasks such as finding the nearest “Mediterranean restaurant”, or figuring out which “Buffalo” you meant by typing it into search, etc. I was recently a guest, on the Heavy Hitters Club (sup, Marco?)… Charity Webinar Series, where I gave a complete talk on “Understanding Schema” which goes into detail about using a proper Entities with a Schema strategy for your SEO campaigns.
Role of Entities in SEO
Knowing that Google is able to identify entities and uses them to classify new content and existing webpages, you can easily predict that we as SEO’s can no longer resort to using thin content and selecting a few keywords for article creation in the future. Instead, we will have to create in-depth content that covers the entire scope and semantic range (topical authority) of any industry that also has valid and the correct entity associations.
This kind of search engine optimization means that Google will be able to recognize a website as an entity in relation to its specific features. Such SEO entities may pop up in search engine results for un-optimized keywords. This is because of the semantic range that helps to present any information that is relevant to a particular search query.
To make it easier for you here’s a list of examples:
- A website that is titled ‘wedding flowers’ can rank well for ‘anniversary flowers’ if Google detects that the content on the website has high quality material describing flowers
- A page that takes up the topic ‘farewell wishes’ may rank well for ‘graduation greetings’ because it uses quality inbound and outbound links that direct to related content
As evident in the examples above, the role of entities in SEO can be identified by looking at the influence they have on SEO ranking.
General SEO Ranking Factors
When you are searching the web, the words you type in the Google search engine bar are the keywords. Contrary to the commonly held view, keywords alone do not determine the SEO ranking. The following are some factors that contribute to SEO rankings and how Google entities are relevant to each factor.
Content Quality
From the SEO perspective, content is seen to be a connection of entities that are related. For example, when you write “Apple is red”, there is a relationship between ‘apple’ and ‘red’ – both of which are separate entities. Since all content is like this, the concept of entities is very critical when it comes to recognizing the amount and quality of the content available online.
Links
With the advent of semantic search engine and the concept of entities, the significance of links has been limited to them being useful signals to other web sources. But it is surprising to see how at their very core, links simulate the function of entities. They pronounce a relationship between different pages on the network. In this way, a link is some sort of a guide that leads you from one entity to another entity of the target page.
Search Intent
Search intent plays a crucial role when optimizing content and determining the ranking. This is because it helps gather information on what users are looking for when they type in the search engine bar. At times it is clear what the user is looking for, but sometimes it is not clear. Google entities help rank the webpage based on how relevant it is to the search intent.
Keywords used often change based on search intents that maybe:
- Navigational
- Informational
- Transactional
- Local Search Intent (Triggers a Map Pack Listing)
For instance, if you pick “Hawaii vacation resorts” as a keyword you want to rank, you will probably think that it would rank higher if you write content for people who are looking for a vacation resort in Hawaii. It is very likely that the people who end up searching for the keyword are buyers of the resort, your content will not be suitable for them and so your page wont rank well.
Google Entity Metrics
According to a Google patent titled, ‘Ranking Search Results Based On Entity Metrics’, the ranking of search results is based on the following four entity metrics.
- Relatedness: The idea that an entity is related to another entity, subject or word. This factor compares instances of co-occurrence and comparing the frequency of two entities being referenced together.
- Notability: This refers to the popularity of an entity in comparison to other entities. It includes social mentions, number of outbound links, etc.
- Contribution: This factor is based on external influence and impact points including fame rankings, reviews, etc. A critical review by a reputable reviewer has a greater impact.
How Can You Increase Entity Value?
If you own an entity and are overwhelmed by the technicalities of SEO entities, some simple ways you can increase the value of your entity are:
- Enhance your content with more related entities to your main topic
- Work on Entity SEO with professional content tools (inLinks, NeuronWriter)
- Get Entity links from Wikipedia and other KG Sources and Google
- Add schema to your webpages and blog posts (Focus on using: SameAs, KnowsAbout, and About & Mentions schema types)
- Find resource pages that are closely related to your main topic and get links from those pages
** PRO TIP: Find your topic in Wikipedia, and pay attention to all of the Blue Links in the article, those are going to be your related entity topics!
Conclusion
With the emergence of entities and RankBrian, Google is on its way to provide the best answers for user queries with the use of semantic search and SGE (search generative experience). We should be moving away from basic keyword research, and doing SEO like we have in the past. Today, it is about related topics, entities and training the search engines to favor us over our competitors. More on that topic very soon, but for now… we hope that you now know how entities:
- Enable Google to accurately prioritize your content with the ranking signals
- Dramatically reduce our reliance on links, and keyword counts, by using Entities and Schema
- Producing better rankings results, by leveraging FAQs, and PAA (People also Ask) questions to get more rich snippets
- Looking direct at the Search Engine Results, to see what Google is looking for in terms of Search Intent and Media Type for Topics or Queries
Your best bet in this age of entity search optimization is to directly analyze how Google responds to your keyword searches in the SERP’s and the type of results it produces (and is there opportunities to create more branded assets, like audio, videos, slides, images, etc). This will help you align your content collateral to what Google is looking for in terms of a search result the end use is looking for. This will maximize the probability that Google ranks you higher than your competitor, and your can begin considering which entities you want on your website by analyzing the top 5 result pages.
Google entities are certainly the future of SEO because of all of the recent Google Updates, and Ai search engine modeling… If you need help understand, or implementing a better Entity SEO strategy for your company, reach out to our expert team of awesome SEOs.




